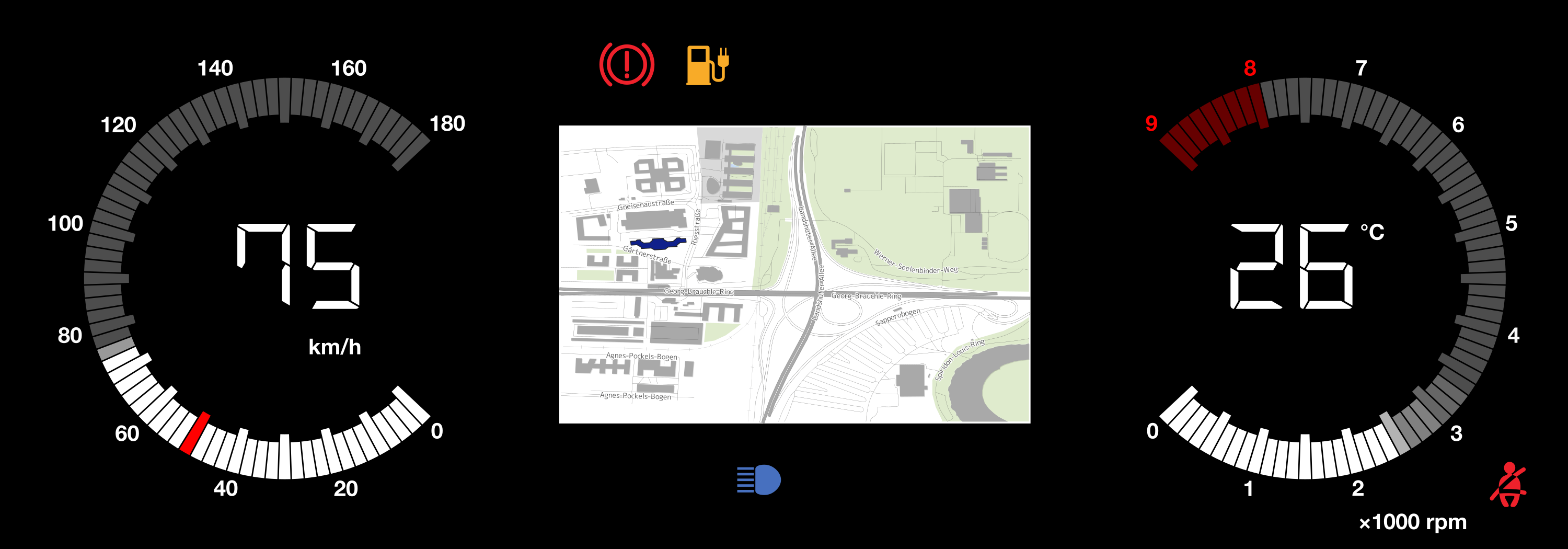
Seiko Epson Corporation has recently begun volume production of the S1D15106, Epson’s first high-grayscale segment LCD driver for instrumental cluster display systems. Epson plans to produce 100,000 of the new drivers per month. The amount of information that needs to be shown on instrumental cluster displays is increasing as vehicles gain additional features and functions.
Larger displays with higher resolution also increase the costs. This has led to an increased demand for cluster displays that can flexibly show part of the content on a TFT display and at the same time show other parts such as telltales or speedometer elements at fixed positions on a segment display.
The S1D15106 is a segment LCD driver that can be directly connected to a microcontroller. Image data transferred from the microcontroller can be displayed on the segment display without an external memory.1 Static driving enables high contrast, while pulse-width modulation (PWM) enables the 16-level grayscale segment display, making this driver ideal for the visualization of things such as speedometers and tachometers.2,3
Furthermore, the driver circuit is equipped with display safety functions such as segment/common output problem (open/short) detection, and if a line from driver output to display is open and a display abnormality is detected, the display can be restored by switching the driver output terminal via control from the microcontroller. The safety functions of the driver circuit support the construction of highly reliable display systems. This driver satisfies the strict quality requirements for automotive products. It is compliant with AEC-Q100 and operates at temperatures up to 105℃.4
Epson seeks to advance the frontiers of industry and drive the circular economy by applying the efficient, compact, and precision technologies that it has developed over many years to solve challenges. These technologies, which save energy, enable smaller products, and increase accuracy and precision, enable Epson to contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which will bring about a better and more sustainable future for all.
Epson also seeks to leverage its device technologies to realize a smart society. Toward this end, the company will continue to develop a variety of controllers and drivers for in-vehicle display systems that require high resolution and safety functions and that enhance the performance of our customers’ products.
| Model No. | S1D15106 |
| Supply voltage | System power supply, VDD: 2.7 V to 5.5 V LCD voltage range, VLCD: 2.7 V to 8.0 V |
| MPU interface | 3-wire serial interface |
| LCD driver | Segments: 368 outputs Common: 1 output |
| Grayscale display | 16 grayscale levels (PWM) |
| Safety functions | Display safety functions |
| LCD driving duty | 1/1 (static driving) |
| LCD driving bias | 1/1 (static driving) |
|
Error detection
|
Command register Segment/common output problem (open/short) detection, etc. |
| Automotive standard | AEC-Q100 compliant |
| Operating temperature range | -40 to +105℃ |
|
Other
|
Built-in oscillator circuit Power-on reset |
| Shipping condition | Bare die (gold bumped) |
1 A microcontroller, or MCU, is an integrated circuit that is primarily used in built-in systems of electronic equipment. An MCU is a type of computer that has been optimized for the control of electronic equipment.
2 Static driving is a method in which the display segment of the liquid crystal panel and the segment terminal of the liquid crystal driver are connected and driven on a one-to-one basis.
3 Pulse width modulation is a modulation method that modules pulse width (= ON time).
4 AEC-Q100: The Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) is an industry group that creates standards for the reliability and qualification of automotive electronics. It was formed by the “Big Three” U.S. automobile manufacturers in partnership with major electronic component manufacturers. The AEC standard is a de facto global standard that has been widely adopted as a standard for automotive electronic components.