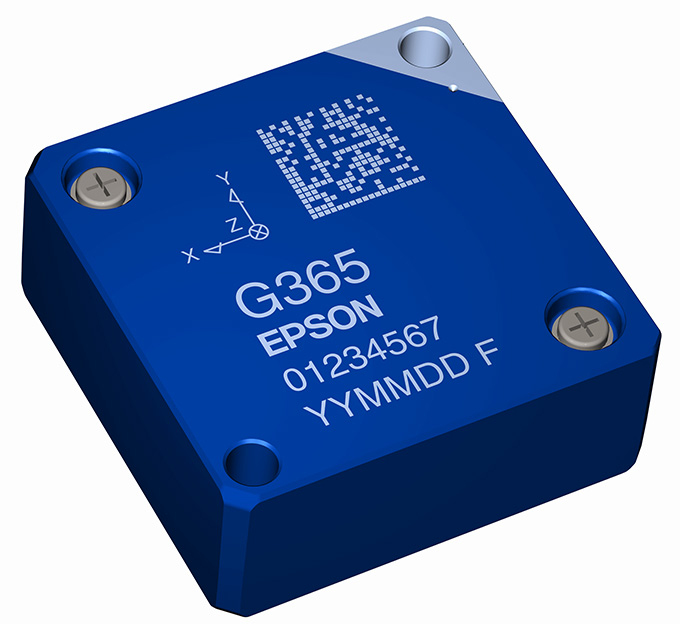

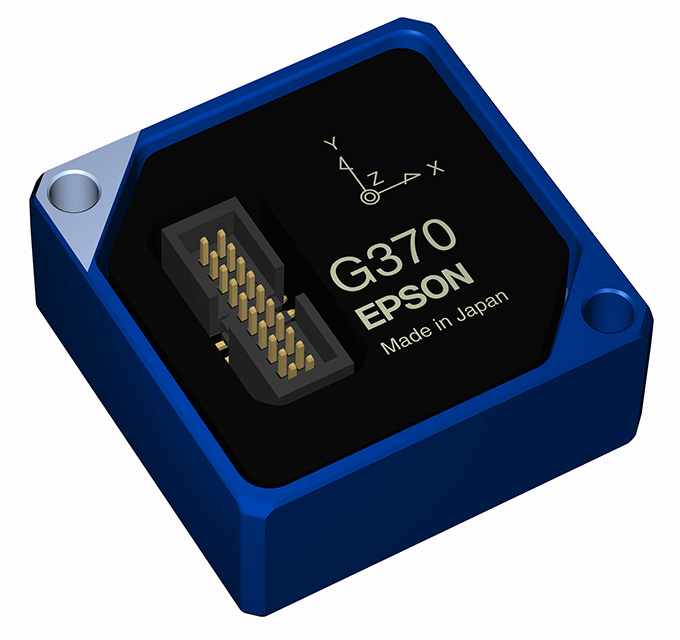
Munich, April 5, 2018 – Seiko Epson Corporation (TSE: 6724, “Epson,”) has developed and recently commenced shipping samples of two new, high-performance six-axis inertial measurement units (IMU)1, the M-G370 and the M-G365. Both models are scheduled for volume production at the end of 2018.
Epson launched its first IMU in 2011. Since then, Epson IMUs have been used in a multitude of applications, earning an excellent reputation for outstanding performance and quality. Rapidly increasing demand from autonomous precision agriculture machinery, intelligent construction machinery and unmanned vehicle applications has fueled demand for high-accuracy positioning in a compact, cost-effective package. Epson’s new IMUs were developed to offer outstanding quality and productivity with the FOG2-class performance needed to realize practicable autonomous driving and navigation. In addition, the new IMUs maintain backward compatibility with the earlier M-G364 and M-G354, making it easy to upgrade performance.
The M-G370 and M-G365
M-G370
M-G365

| Product number | M-G370 | M-G365 | |
| Rate range | Triple gyroscopes | ±450 °/sec | |
| Tri-axis accelerometer | ±4G / ±10G | ||
|
Accuracy and |
Gyro bias instability | 0.8 °/hr | 1.8 °/hr |
| Angle random walk | 0.06 °/√hr | 0.08 °/√hr | |
| Scale factor non-linearity |
Triple gyroscopes | 0.05 %FS (<300 °/sec) | |
| Tri-axis accelerometer | 0.1 %FS (<5 G) | ||
| Internal compensation at factory (compensated temperature range: -40°C to 85°C) |
Bias, scale factor, misalignment (axis to axis) | ||
| Output data rate | Up to 2,000 Sps | ||
| Calibration & operating temperature range | -40°C to +85°C | ||
| Current consumption | 16 mA @ 3.3 V | ||
| Orientation angle output | – | Tilt angle (X & Y axes) Euler angles (Roll & Pitch) |
|
| Other features | External trigger input, etc. | ||
| Size | 24 x 24 x 10 mm | ||
| Weight | 10 g | ||
* These specifications are subject to change without notice.
Please see the link below fur further details about these products.
https://global.epson.com/products_and_drivers/sensing_system/
1 An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is a device that is used for sensing inertial motion. It is comprised of 3-axis angular rate sensor and triaxial accelerometers.
2 A fiber optic gyro (FOG) is a type of gyroscopic sensor based on optical fiber and the properties of light interference that can be found in some high-performance IMUs.
3 A gyroscopic sensor (angular rate sensor) measures the rotation angle (angular rate) of an object versus a reference axis per unit of time.
4 Gyro bias instability is a measure of random variation in gyro output bias as computed over a specified sample time and averaging time interval, the variation of the bias being characterized by 1/f noise density.
5 Angle random walk is a measure of random variation in gyro output bias as computed over a specified sample time and averaging time interval, the variation of the bias being characterized by random noise density.
6 A digital signal processor (DSP) is an arithmetic circuit for high-speed processing of digital signals.
7 The extended Kalman filter, which uses model-based estimates and actual observed values to sequentially calculate the most probable values, are used to more accurately predict information from observed values that include filter errors.
8 Orientation angle (roll, pitch, and yaw):
9 A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is a satellite system that is used to pinpoint a geographic location anywhere in the world.
10 Inertial navigation system (INS)